✨ Lesson 5 – Transmission Media, Waves, Wireless Propagation
🎯 0. Overview of Lesson 5
Lesson 5 builds on Lesson 4 by going much deeper into:
- Why twisted pair works (magnetic field cancellation)
- How coaxial shielding works
- How fiber optic cables guide light
- Burst noise
- Waves, wave formulas, and electromagnetic spectrum
- Wireless propagation methods(: refers to the transmission of electromagnetic signals through various media)
- Wireless networks and signal attenuation
🧵 1. Twisted Pair (UTP / STP)
🔵 1.1 The Anatomy
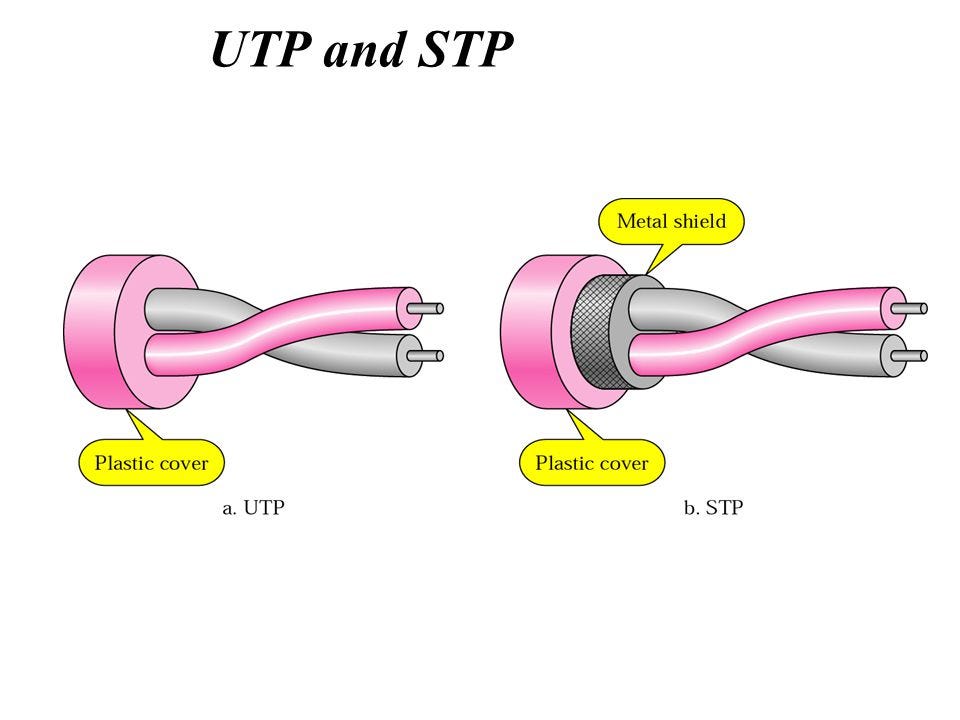
- Pink wire = carrying the actual signal ➜ current produces a magnetic field
- Gray wire = intertwined with the pink wire ➜ carries an opposite current
When wires twist around each other, they form: ➡️ Equal & opposite magnetic fields → cancel each other → reduced induced noise
This is called induction cancellation.
🌟 1.2 Complete Explanation
- Current in any conductor produces a magnetic field.
- Changing magnetic fields induce voltages in nearby wires (this is called inductive coupling).
- By twisting the wires, each wire experiences equal exposure to external fields.
- Because each twist alternates which wire is closer to noise sources, interference cancels out.
📌 Result:
- Less noise
- Less crosstalk
- More stable digital signals
🆚 1.3 UTP vs STP
- UTP (Unshielded) → only twisting for protection
- STP (Shielded) → adds a metallic shield around twisted pair
📡 2. Coaxial Cable
🧩 2.1 Anatomy
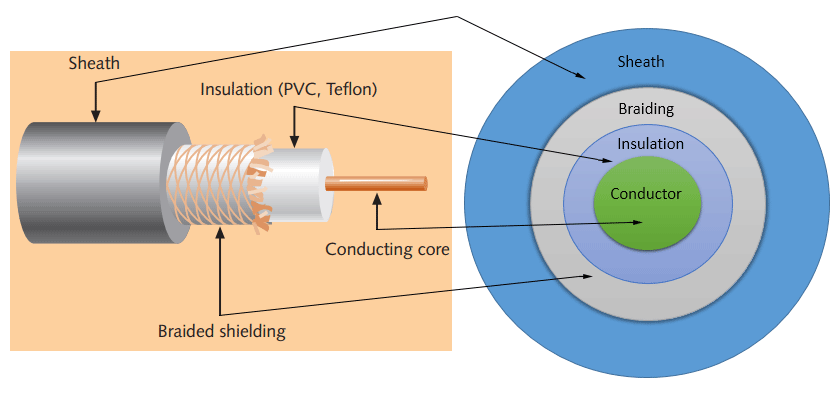
- Copper core inside
- Surrounded by an insulating dielectric
- Surrounded by a metal mesh shield (looks like a fence)
- Outer jacket
The mesh shield absorbs and cancels external magnetic fields.
🎯 2.2 Full Explanation
Coax gives 360° protection because:
- The braided copper shield carries induced currents
- These induced currents generate an opposing magnetic field
- The opposing field cancels incoming interference → excellent EMI resistance
Coax is used for:
- Cable TV
- Radio antennas
- Security cameras
- Some internet modems
💥 3. Burst Noise
⚡ Burst Noise = when N consecutive bits in a signal are corrupted.
- Not just one bit flipping
- Caused by strong interference lasting multiple bit intervals
This is important for error detection & correction in digital comms.
🔦 4. Fiber Optic Cable
The professor clarified there are 3 layers
🧱 4.1 Anatomy
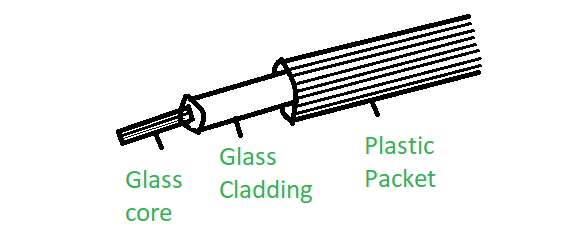
- Outer Jacket — thick, opaque, protects against environment
- Cladding — transparent layer, lower refractive index
- Core — transparent, higher refractive index
🌈 4.2 Why light stays inside the core
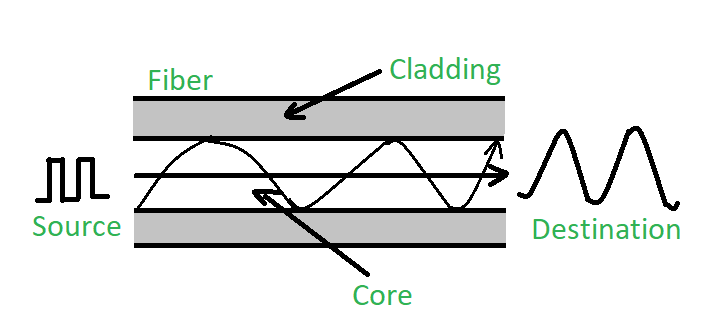
Because of Total Internal Reflection (TIR).
Light travels inside the core and tries to escape, but…
- The cladding has a lower refractive index
- So the light is reflected back into the core
➡️ Light “bounces” through the fiber like this:
🔊 4.3 Noise in Fiber
Noise = unwanted light entering or leaking out of core.
- Could be due to bending, breakage, or poor connectors.
Fiber is immune to electrical noise.
🌊 5. What is a Wave?
➡️ Oscillation of a charged particle
The movement of this oscillation creates EM waves.
📐 5.1 Wave Formula
y(t) = A · sin(2πft + φ)
Where:
- A = amplitude (height)
- f = frequency (Hz)
- φ = phase (shift)
And:
c = f · λ
Where:
- c= Wave speed, measured in meters per second (m/s).
- f= Frequency, the number of wave cycles per second, measured in hertz (Hz).
- λ= Wavelength, the distance between two consecutive points on a wave (like crests), measured in meters (m).
📏 5.2 Relationship Between λ, f, and c
λ = c / f
Where:
- λ = wavelength
- f = frequency
- c = wave speed (depends on medium density)
📡 6. Electromagnetic Spectrum
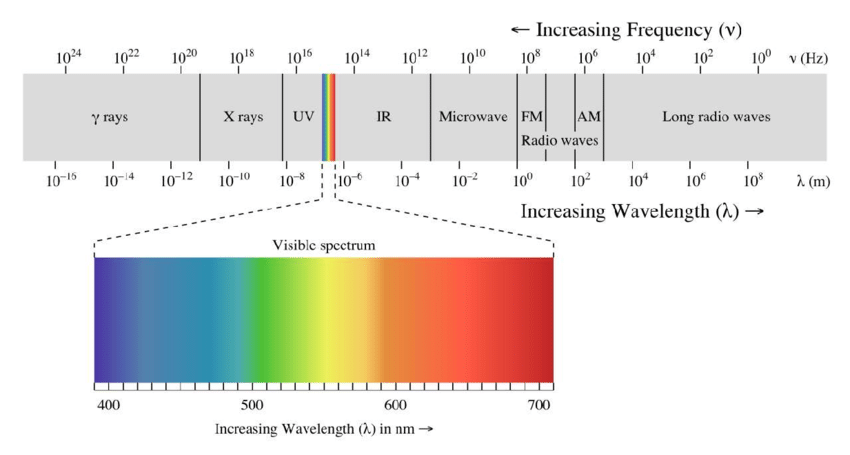
🌈 EM Spectrum Regions (in order)
- Gamma Rays
- X-Rays
- UV
- Visible (400–700 nm)
- IR
- Microwaves
- Radio (FM → AM → Long Wave)
📡 6.1 Wave Behavior by Frequency Range
🔵 10³ – 10⁸ Hz (low frequency)
- Waves spread in all directions → spherical
- Very long wavelength
- Travel far, penetrate well
🔵 10⁶ – 10⁸ (Radio)
- Also mostly omnidirectional
- Includes AM, FM, etc.
🟣 Microwaves (10⁸ – 10¹²)
- Directional
- Need line-of-sight
- Cannot pass solid objects well
- Used in: Wi-Fi, radar, satellites
🔴 10¹² – Visible
- Includes IR, visible, UV
- Can pass some hard materials (like glass)
📌 Bluetooth
- 2.4 GHz (microwave band)
- Between FM and microwaves
🧠 6.2 Additional useful facts
- Higher frequencies → more data, more attenuation
- Lower frequencies → long range, lower bandwidth
- Microwaves used for point-to-point links
- UV is blocked by atmosphere
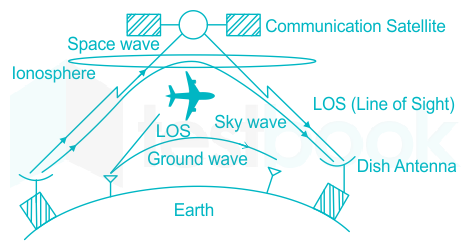
🛰️ 7. Wireless Propagation Methods
The main ones are:
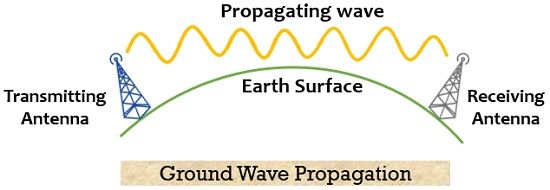
🌍 7.1 Ground Wave Propagation
- Follows curvature of Earth
- Good for long-wave radio
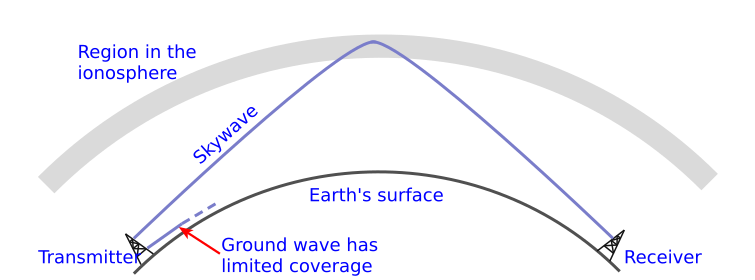
☁️ 7.2 Sky Wave Propagation
- Signal bounces off the ionosphere
- Used by shortwave radios
🛰️ 7.3 Satellite / Line-of-Sight
- Signal goes to satellite and back down
📶 8. Wireless Networks
There are two types:
🏢 8.1 Infrastructure-Based Networks
- Use access points, routers, boosters
- Coverage area depends on signal strength
📉 Signal Attenuation Diagram
Amplitude decreases with distance:
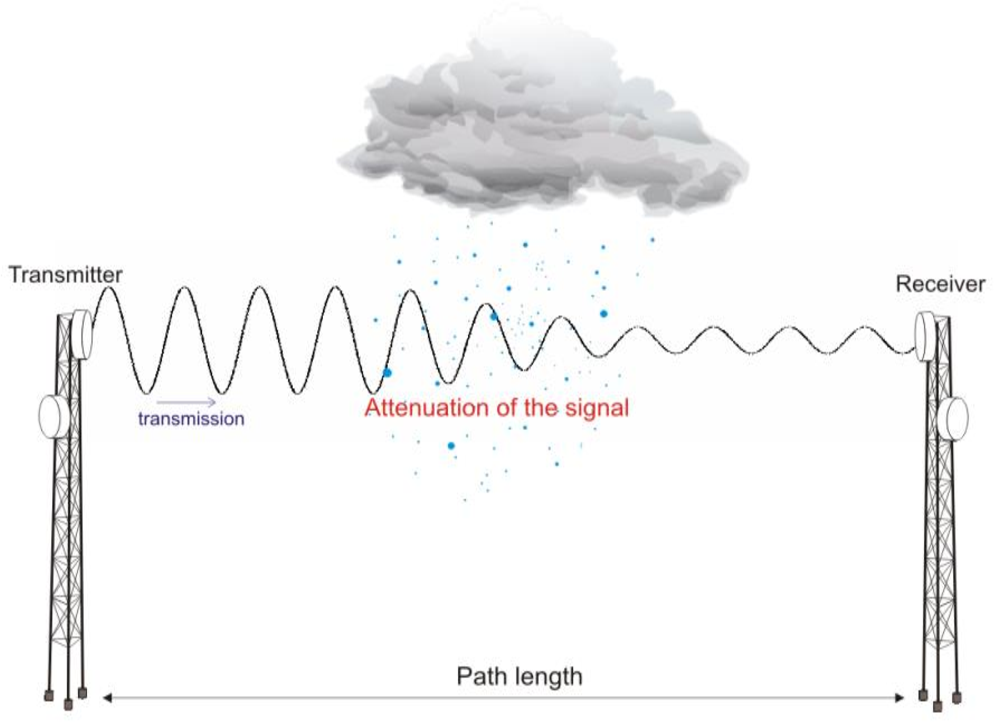
Why? Because energy spreads out and is absorbed.
Boosters repeat and strengthen the signal.
🤝 8.2 Ad-Hoc Networks
- Devices connect directly
- No access point
- Range limited by device power
🏁 FINAL SUMMARY
Lesson 4 foundations → Lesson 5 deep explanations:
- ✔ Twisting = magnetic cancellation
- ✔ Coax = shield-induced cancellation
- ✔ Fiber = refractive index + total internal reflection
- ✔ Wireless propagation (has 3 types)
- ✔ Wireless Networks (Infrastructure vs Ad-hoc)